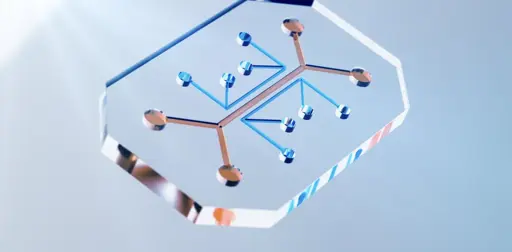
In 1999, researchers found that these tiny electrophoresis systems could also separate intact pathogens by differences in their electrical charge. They placed a mixture of several types of bacteria in a very thin glass capillary that was then exposed to an electric field. Some bacteria exited the device faster than others due to their distinct electrical charges, making it possible to separate the microbes by type. Measuring their migration speeds allowed scientists to identify each species of bacteria present in the sample through a process that took less than 20 minutes.
You must log in or # to comment.