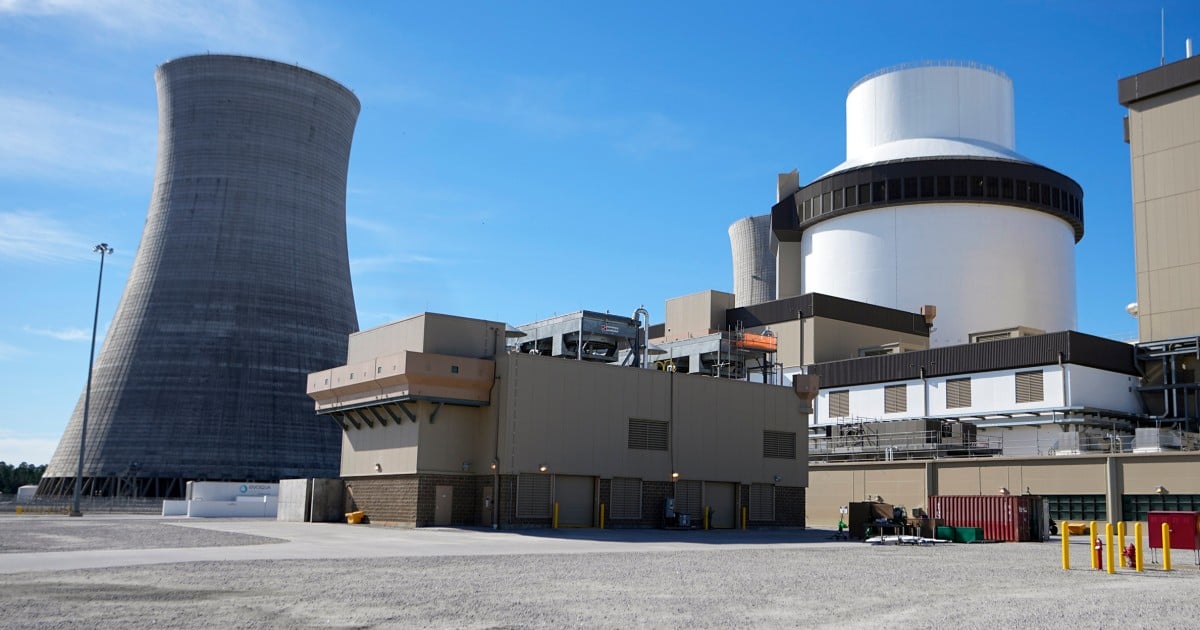
First U.S. nuclear reactor built from scratch in decades enters commercial operation in Georgia::ATLANTA — A new reactor at a nuclear power plant in Georgia has entered commercial operation, becoming the first new American reactor built from scratch in decades.
Good news. Anything but fossil fuels at this point.
The reduced operating emissions take 10+ years to outweigh the enormous construction emissions of nuclear. (Compared to gas.)
Fortunately the nuclear reactor can be operated for >50 years :)
Mean and median lifetime of a nuclear reactor is well under 30 years. Closer to 20 if you count all the ones that produced for 0 years.
Sure. But do you think Nuclear reactors will still be cheaper than renewables + storage in the 2070s? Nuclear is far more expensive per kWh than renewables, and the cost of storage is falling fast.
Good question, that one can only speculate on. IMO it’s a two part question.
First is that newly built nuclear plants are expensive. So the question depends on if we bite the bullet (build the reactor) today or in 2070. One built today will produce cheap power in 50 years.
For example in Finland we have reactors from 1980, that make up the backbone of stable energy production in our country. Those are going to be kept online till the 2050s. I’d argue at that point the cost per kwh will be mostly dependent on maintenance and fuel, so relatively small.
Wind and solar cannot reap the same benefits if you have to replace the plant every 20 years.
Storage is a completely separate question that is not taken into account when new wind farms and such are being built. If one was to account for storage today, the cost of renewables would be much closer to that of other means of production.
Also in the future, if storage costs keep falling due to billions of R&D money, similar effects could be achieved in nuclear via serial production and scale.
EDIT: Just read you have studied this stuff for real. Then ignore most of what I said, as you might know better :D
The cost of the power it generates in 50 years aren’t lower than the day it opens. If you amortise the cost of the plant over its life nuclear is stupid expensive per watt produced. It’s expensive enough that renewables + storage is cheaper. Renewables + storage is also a lot quicker to build than nuclear.
Even after the uptick in cost of renewables in the last year (which was dramatic) they’re still the cheapest new build power (even accounting for the integration costs). As an example here’s the most recent annual csiro report on energy costs by type. It doesn’t include full scale nuclear today because it’s known to be unviable, but even 2030 projections on “if smrs are commonly deployed at scale” they’re predicted to be a lot more expensive than renewables with integration costs.
https://www.csiro.au/en/research/technology-space/energy/energy-data-modelling/gencost
I would say it’s not the BEST solution but in areas in the extreme north/south, where solar/hydro aren’t options (and I legit have no idea how well wind would do with freezing weather/snow etc) it would be better to have nuclear there than to try and transmit long distance to those areas. At least until we get some more breakthroughs in energy storage.
deleted by creator
I literally studied this exact nuclear design at University - the Westinghouse AP1000. You can look up the WNISR (World Nuclear Industry Status Report) if you don’t want to take my word for it.
Don’t forget, mining and enriching uranium still has a significant carbon footprint, far higher per tonne than any fossil fuel. Yes, it’s lower over time, but we need to be reducing emissions now, not in 50 years time.
Yeah I hate how laxness about fixing this in a timely manner has somehow convinced some people that shit like “carbon nuetral by 2070” is ok and helpful. And I’m just remembering when that study came out that said the climate as we know it is probably gone forever if we aren’t totally carbon nuetral by at least 2030
deleted by creator
Why are you comparing fossil fuels and nuclear “per tonne” that makes no sense. You replace tens of tones of nuclear fuel per year any you burn millions of tones in a comparable fosil fuel plant.
And regarding the carbon emissions from enrichment… Just use nuclear to power your enrichment plants. This way your emissions are extremely low because you don’t need much fuel and you use nuclear energy to produce nuclear fuel. French example: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tricastin_Nuclear_Power_Plant
Why compare per ton of fuel when per kWh would be the more meaningful metric?
What are the cradle-to-grave emissions of a nuclear plant, vs a fossil fuel plant, per kWh generated. That is a far more honest question, and I’m inclined to err on the side of nuclear.
Let’s not forget radiation caused by the power plant. Nuclear produces far less radiation than a coal plant.
deleted by creator
So you’re saying the construction effort requires at least a decade of nuclear powered energy to be achieved?
That could be up to 3.652 TWh. That’s more than my entire nation consumes in three years and we’re one of the world’s biggest suppliers of natural resources, including nuclear.
You’re mathing wrong.
Nuclear is still fossil fuel, just not combustion. But I agree, this is good news because it helps reduce coal and gas usage.
Edit: I get it, I’m wrong. No need to repeat the same comments over and over.
I’m confused by your definition of fossil fuels.
It’s the fossils of stars.
Nuclear is Non-renewable, but it’s not a Fossil fuel:
A hydrocarbon-based fuel, such as petroleum, coal, or natural gas, derived from living matter of a previous geologic time.
We have plenty of nuclear fuel and waste is a drop in an ocean compared to that of fossil fuels.
Yep. This is why I’m annoyed the UK is dumping its money into oil and coal fuel sources. We need more Nuclear plants and we should have started building these yesterday.
The best time to
plant a treebuild a nuclear power plant was 20 years ago. The second best time is now.
I’d prefer it if my nuclear waste doesn’t drip into the ocean, please /s
What’s your favorite dinosaur? Mine is the Plutonidon
Natural predator of the laser raptor
Ooh a lot of people here seem very pro-nuclear-power. That’s cool!
Unfortunately, there’s still that one guy in the comments trying to say that hypothetical, largely unproven solutions are better for baseload than something that’s worked for decades.
That or the fear-mongering talking points. That’s what caused our local power plant to be decommissioned, and now those same people are complaining about how much their electrics cost now.
The old soviet legacy. And a bit of actual disasters and from the 2 significant ones (hiroshima and chernobyl) half are beacuse of the soviets.
*Fukushima
Hiroshima was the freedom bombing disaster
on a side notw how people have dies from fukushima in the years since and how many have died from coal? Also you can compare the number of long term health problems
Doesn’t matter. Bad news at the time was enough to scare people for the next 30 years.
Heck, even my college Sociology textbook from OpenStax basically has nuclear fear-mongering baked into one of the later sections.
some people can’t help but cut their nose to spit their face
I think you mean hypothetical technology that hasn’t been invented yet, but he expected will be in widespread use 50 years from now.
If you mean renewables by that, it’s hardly hypothetical or unproven. I’m in Australia and south Australia and Tasmania (two of our states) have fully renewable grids, Tasmania for the past 7 years. South Australia does still occasionally pull from an interconnect but most of the time they’re exporting a bunch of power.
Renewables with storage are cheaper and faster to build than nuclear and that’s from real world costs. Nuclear would be fine if it wasn’t so stupidly expensive.
Tasmania
Generates nearly all its power using hydro electric, which is great but pretty dependent on geography.
South Australia
Wiki says a pretty big hunk of that is still gas
In Ontario Canada where I am from it would take > 4000 wind turbines all working at once (not including the batteries) to supplant our nuclear capacity. Even the largest battery storage are in the hundreds of mega watts and only for a few hours at the cost of about half a billion dollars.
I think it is more productive to approach these technologies as complementary as any proper grid should have both for the near future if we want to reduce global warming.
Ah sorry, my mistake on that one. Despite how many wind turbines working at once it may take, the power from the is cheaper by a long shot than nuclear.
The reason I don’t think nuclear is the main solution is just cost + build time. It’s horrendously expensive. Much more so than the cost of renewables with proper grid integration (transmission, storage etc.) that has been modelled.
Maybe in a while the small nuclear reactors may come close, but currently the full sized reactors are too expensive and smr’s aren’t really a thing yet because of cost.
If power prices can come down instead of go up it’s going to be a lot easier to convince everyone to transition away from fossil fuels, and from modelling that’s been done (e.g. by csiro) that can be the reality
The nuclear lobby is alive and well on social media. Never before has the internet apparently agreed on something so controversial with some of the most cookie cutter, copy and paste, AI generated comments on the subject I’ve ever seen.
The talking points seem to gloss over the fact that nuclear storage always fails, meltdowns happen, and you still have to mine uranium out of the ground. It’s far from a clean source of energy.
That the “nuclear lobby” is paying people to post stuff on Lemmy, a social media platform that accounts for a small part of single percent of all social media users, is a hot take I haven’t heard yet. Congrats, you’ve definitely imagined a scenario that nobody else in history has ever thought of. A true original thought.
Pity it’s an absolutely fucking brain dead take masquerading as something more than nonsensical blithering from a total nincompoop, but you should bask in this moment nonetheless.
It’s not the cleanest, but in term of CO2 and other toxics produced per Giga-Watts, it’s the best compromise.
Fission is hopefully, coming in the next decades. Like the other guy said, anything but coal/petrol.
Oh wow really? Hope it kicks off some good news for other plants in the future.
The good news - it’s online, generating clean power, and hopefully demonstrating the safety and benefits of modern nuclear plants.
The bad news - it’s $17B over budget (+120%) and 7 years behind schedule (+100%). Those kind of overages aren’t super promising for investors, but perhaps there are enough lessons learned on this one that will help the next one sail a little smoother.
Either way, good to see it can still be done in the US.
What’s the normal amount of over budget and behind schedule?
Ideally zero? But given this is the first US reactor in decades, it is by definition normal I suppose.
Those amounts there. For comparison for example another recent plant Olkiluoto 3 in Finland was 13 years late on a 5 year original construction timeline (18 years total construction time) and
108 billion euros over budget on original budget of 3 billion euros. (Final estimate it cost constructor13-1411 billion euros to build. Technically its fixed price contract so customer price is still 3 billion. However it did bankrupt the builder Areva and litigations are ongoing about, if the French can extract more money from he customer TVO)So doubling the price budget and doubling the build time is not at all unreasonable first estimate on the announced numbers of the builder and customers at start of project.
Also, according to the story, power costs will go up as a result of this reactor coming online.
True, BUT the cost increase was relatively small (~$3.50/mo) - can’t speak for everyone as I know people’s budgets can be quite tight right now, but that’s a price I’d be willing to pay for more nuclear on my grid.
I wouldn’t call it “clean power”. We still don’t have a good solution for the nuclear waste.
Edit: Downvotes because I am not religiously defending a technology and pointing out that there are downsides (EVERYTHING HAS DOWNSIDES!). Too many people from reddit here already.
Sure we do, put it in the holes we took the other stuff out of. Soon our whole planet will be nuclear powered.
Compared to the downsides of virtually every alternative energy source, the downsides of nuclear are peanuts.
In finland we have this big hole that goes half a kilometer into stable bedrock. The storage solution is engineered to withstand the next ice age.
It’s Finland, haven’t you been in an ice age for the last 1000 years?
I guess this is a joke, but regardless. The current climate is quite different from having an ice sheet 3km thick on the ground. This summer we were nearing 30°C/85°F on some days.
Nuclear power plant waste doesn’t significantly contribute to climate change or pollution? So it’s “clean” by most metrics.
Nuclear waste can generally be stored on-site without issue. Reprocessing would be nice, but not even necessary. Just because you don’t understand the problem, doesn’t mean others are “religiously defending a technology.”
Coal was also considered clean in the beginning because they didn’t have to sacrifice forests anymore.
We may not consider the waste a problem now, but that may very well look differently in 50 or 100 years.
Again: I am completely fine considering nuclear power as one of the best options we have. I am not so fine pretending it’s without tradeoffs, because that would ignore how any other form of energy generation in the past/ever finally turned out.
Yeah, this is one of those topics where any mention of the downside of storing spent fuel safely for 50-100,000 years gets you bombed on. Just like reddit.
Yes, we do. Burying it works just fine.
That’s not a solution. That’s a workaround.
And why is that exactly? Decay means the problem will solve itself, all we need to do is keep the waste away from the outside world until then.
This would be a great solution if nuclear waste was a one-time non-reoccurring problem. More waste will be produced continually, and if more nuclear power plants are built to match energy demand, a lot more waste, multiple times more. Eventually we will run out of places to put it, and then of course also deal with the fact that every abandoned old mine or cave in the world is full of radioactive material.
The closest “bury it in a hole” can come to a permanent solution is if the hole is on the moon or something. Even then there are downsides. Do you know how expensive it is to dig giant holes?
You are vastly overestimating the amount of waste a reactor produces. Look up some figures on the internet. There is no way we will ever run out of space to put it.
deleted by creator
The plan, called Cigéo, would involve placing the waste 500 metres (1,640 ft) below ground in a clay formation in eastern France.
Construction is expected in 2027 if it gets approval. Among those opposed to it are residents of the nearby village of Bure and anti-nuclear campaigners.
Burrying waste is not exactly clean. Yes, they reduce the waste. But they are also hitting limits and have challenges in increasing capacities.
In spite of the war in Ukraine, which has made many in the West avoid doing business with Russia, EDF is expected to resume sending uranium to Russia this year as the only country able to process it. It declined to confirm to Reuters it would do so.
That is also not really cool. I also find it a bit shady that something is only doable in Russia. That sounds a bit like it’s only possible there, because they ignore safety rules any other country would have in place and we don’t care because “now it’s their problem”.
deleted by creator
But we don’t have that solution yet (see above). That’s like hanging on the idea of having nuclear fusion available. Yes, theoretically nice, but until they are practical, we shouldn’t count on it.
Yes, theoretically the “waste” of current reactors still has energy to be harvested. But practically we can’t use them to a degree where there is no waste afterwards.
For the past decades and sitll ongoing, fission reactors are not clean (also decomissioning them leaves a lot of unusable waste; and they have to be decomissioned at some point).
Also from what I know, extracting the nuclear material from the earth and preparing it for use in a fission reactor is not very environmentally friendly either.
Is nuclear better than coal? Very likely. But it’s not clean.
Let it run 5 months and the money is back in.
Not really. All costs considered, nuclear is one of the most expensive energy sources.
Darn all those superfluous safety regulations. If only we could make them cheap and fast and not worry about radioactive contamination like the coal industry.
Seriously though, start enforcing adequate regulation on the other sources of life threatening power generation and watch the costs even out.
Coal isn’t the cheapest though. For new build power renewables + storage are. That is to say, the incremental cost of running a coal plant isn’t that massive, but cost to build + fuel one amortised over the lifetime is more than renewables + storage.
So yes, you can enforce “adequate regulation” and nuclear will still be the most expensive.
Yes, but nuclear scales the best, requires lower geological footprint than renuables, and is safer than fossil fuels. Price is not the only metric of value.
deleted by creator
Oh I think we should shut down coal as soon as possible. But if energy prices can go down by having the cheaper energy production of renewables instead of up because of nuclear the transition can happen faster.
Yes nuclear power plants are very expensive. But the energy density is phenomenal.
Energetic armortisation is far quicker on a nuclear plant than on solar panels.
And the argument of subsidies is usually a fake one, since governments also pour millions into renewable energies.
Broken down to lifetime cost to the cost of comparable technologies, nuclear is still on the same level as solar and wind.
Since I am from Germany, and German sources might not be ideal to share, let me explain it this way: People are not stupid. They will never choose the financially unwise option, if the other one would seriously be the better one.
People are not stupid. They will never choose the financially unwise option
I see you’ve never been to the U.S.
Ok. Valid argument.
But while Germany quit nuclear power, the rest reinforced their standpoint.
Thousands of scientists from different countries all agreed upon nuclear power to be a reasonable source of energy. Even a Japan is still going forward with nuclear power. It is only Germany, which made an emotional choice, Merkel wanted to please the masses. And here we are now. Burning coal, as if we were thrown back into the industrial time, forced to use primitive methods to produce energy.
Can you find any recent analysis that supports your claim that nuclear costs are at the same level as solar?
The only one I’ve seen suggest this was from a nuclear industry lobby group, and it inflated the costs or solar by insane amounts.
In Australia this is a bit of a hot topic and all impartial estimates suggest that nuclear will not get close to renewables in any way, even taking into account storage and grid costs.
In the 10 years since this single reactor was built, one of our states has transitioned to almost 100% renewables. Wholesale costs have plummeted, but renewable projects are still profitable in the market. I was involved in a reactor project in a western nation some time ago (it’s still being completed unsurprisingly), and the lock-in wholesale price to support that project was simply extortionate. Solar generation prices are a whole magnitude smaller.
This is a German source that incorporates many studies and presents their results. Some agree with my statement, some with yours. But fact is, that the financial difference is very small.
Page 23 for example suggests my statement.
On page 32 you can see the development that suggests that you are right.
But considering the costs for the expansion of the energy grid, battery storage systems, and the rising production costs of everything, I believe Nuclear to be the cheaper option and the far more reliable one.
People do often act stupid, but you are seeing it from what I consider to be an incomplete perspective. Nuclear could be financially unwise overall, but someone would still get a payday. That 17B over budget wasn’t burned and unmade, it went into the pockets of the people organizing and building the power plant.
All this to say, the huge majority of the people involved in making the power plant a reality weren’t motivated by the efficiency of the power production on a cost basis. Most of them were probably making more money while it was still being subsidized, planned, and built. And while I think subsidies are generally useful and good, they can be a vector of financial abuse when it comes to unprofitable industries.
Lastly “lifetime cost” is a bit of a useless metric when the majority of that lifetime comes too late. No point to a power source that will cleanly produce power after it has meaningfully contributed to pushing us over the edge and past the breaking point for a climate that can support agriculture as we know it. There isn’t enough time or margin for error in emissions left available to build all the nuclear plants needed to meet energy demands.
About damn time! As a Georgia Power ratepayer, I’ve only already been paying for it for what, around a decade now?
That’s the downside of nuclear. Cost and build time. Upside is it’s reliable and carbon-clean.
The best time to build a nuclear power plant was thirty years ago. The second best time is now.
They took the average of that and built it 10 years ago
The 1.3th best time to build a nuclear power plant was 10 years ago
This encapsulates the public response to building nuclear. I guess that is why it is the first in decades.
To be clear, my comment isn’t “the public response to building nuclear;” it’s “the public response to corruptly financing nuclear on the backs of ratepayers while guaranteeing zero-risk profit for shareholders, despite incredible incompetence and cost overruns building the thing.”
If you think that bullshit is inherent to building nuclear, I won’t dispute it, but I will say it makes you even more cynical than me!
I would’ve had no problem with it at all if it weren’t a fucking scam to gouge me for somebody else’s profit.
Oh, neat. My state did something not completely stupid. I’ve got some reservations about nuke power as opposed to renewable, but this is definitely better than continuing fossil fuels.
Fission and fusion reactors are really more like in-between renewable and non-renewable. Sure, it relies on materials that are finite, but there is way, way more of that material available in comparison to how much we need.
Making this distinction is necessary to un-spook people who have gone along with the panic induced by bad media and lazy engineering of the past.
Fusion and fission are quite different. A practical fusion reactor does not exist. It’s outside our technological capability right now. Current fusion reactors are only experimental and can not maintain a reaction more than a small fraction of a second. The problem is plasma containment. If that can be solved, it would possible to build a practical fusion reactor.
The fuel for a working fusion reactor would likely be deuterium/tritium which is in effect unlimited since it can be extracted from seawater. Also the amount of fuel required is small because of the enormous amounts of energy produced in converting mass to energy. Fusion converts about 1% of mass to energy. Output would be that converted mass times the speed of light squared which is a very, very large number, in the neighborhood of consumed fuel mass times 1015.
Fusion is far less toxic to to the environment. With dueterium/tritum fusion the waste product is helium. All of the particle radiation comes from neutrons which only require shielding. Once the kinetic energy of the particles is absorbed, it’s gone. There’s no fissile waste that lingers for some half life.
deleted by creator
Here’s something more interesting. A matter-antimatter reactor converts 100% of mass to energy so it’s a hundred times more efficient than fusion. In modern times antimatter has been produced at quantum levels in large accelerators such as the Hadrian collider. So it does in fact exist and can be produced.
However a matter-antimatter reactor has some serious technical problems. For one it’s currently impossible to create antimatter in any practical quantity. Second if antimatter comes in contact with matter, instant boom. Like a sugar cube size of the stuff could level a large city. So containment would be an insurmountable problem.
The interesting part is when you see an antimatter reactor in shows like Star Trek, it’s based on real science. Interestingly in 1968 when they wrote the original Star Trek, nobody knew antimatter was a physically real thing. That’s a case of sci-fi predicting science.
deleted by creator
But antimatter needs energy to create, probably more energy than it can produce. Unless you can find some source of it in the environment. Fusion is much more likely.
Antimatter might make a good compact way to store energy for a starship, if it was created in a large fixed facility with access to huge power sources. But it’s not a way to generate energy by itself.
Your info is a little out of date - some fusion experiments have been able to maintain fusion for almost a minute. However, your point still stands. We are decades away at a minimum untill a viable fusion reactor.
My guess is that fusion will be too expensive for commercial use unless they can get a super compact stellarator design to produce huge amounts of energy, and make them cheap to build (HA!).
Or we will see them in spaceships. :P
I was just future proofing my comment for things like this: https://youtu.be/_bDXXWQxK38
Here is an alternative Piped link(s): https://piped.video/_bDXXWQxK38
Piped is a privacy-respecting open-source alternative frontend to YouTube.
I’m open-source, check me out at GitHub.
Sure, it relies on materials that are finite, but there is way, way more of that material available in comparison to how much we need.
Not trying to be “difficult,” but isn’t that what people thought about coal/oil at first? I understand that the scale is different, but it still needs to be a stop gap as opposed to a long term plan.
Spent Nuclear Fuel, unlike coal or oil, can be recycled to a certain extent (this is done in places like France but not the US). If we recycled all of the spent fuel, we’d potentially have a thousand years (give or take) of fissionable fuel. Plenty of time for us to get fusion running so we can completely wean ourselves off petroleum energy generation.
You’re conflating leftover dregs of Pu-239 (about a 10-15% boost in energy per fuel input) with non-fissile material like U238. Breeder reactors required to use the second have never been used commercially in breeding mode.
You’ve either fallen for or are intentionally spreading a lie.
What lie am I spreading? Conventional Light Water Reactor Nuclear Fuel (5-6% U-235 w/t%) can be recycled. This can be done even without using breeder reactors which operate through fast fission of U-235
Yes the plutonium van be stripped out along with the other transuranics, and it does pose a proliferation risk (separate issue), but it definitely can be recycled. France reprocesses their fuel.
Ah. So intentional then. You’re trying to pretend extracting the <0.7% left over U235 and Pu239 (for a 10-15% increase in U235 fuel economy) is somehow fissioning U238.
I don’t understand what you’re trying to say here. Reprocessed fuel does not imply that we’re now fissioning U-238. That takes place in a completely different energy regime (fast fission vs. thermal). Light Water Reactors and fast reactors operate differently, with different fuels. LWRs in commercial operation use slightly enriched U-235. There is no fissioning of U-238 other than the very small amount of spontaneous fission which is negligible compared to contributions from thermal fission in an LWR. The Six Factor formula governs criticality reactions, and these terms differ for both reactor types. The nuclear cross sections are fundamentally different between these energy regimes.
Reprocessed fuel is what it implies, recycled processed LWR fuel, stripped of the fission products that built up as the fuel underwent burnup in the core. If this were some sort of pretend activity then I guess the entire reprocessing back end of the nuclear fuel industry is fake.
I don’t appreciate the personal attacks, so if you have nothing constructive to say, good day to you sir slash madam.
U-238 is largely stable and has the consistency of metal, making it easy to store or sequester away. Most natural deposits of Uranium are U-238.
Additionally you can make a breeder reactor that bombards U-238 to make U-239 which has a half life of 23+ minutes and decays into Plutonium-239 which can be used in nuclear power generation.
billions if we start using thorium
So far the problem, if I understand correctly, is all thorium reactors are molten salt reactors. The issue there is, we still haven’t solved the metallurgy problems of dealing with the corrosive salt. It destroys all the pipes. We have slowed it down, but not enough to go production with.
Why do you think we need nuclear to transition fully off petroleum? Renewables with storage are cheaper today for new build power, let alone in another 20 years. They continue to get cheaper and more efficient quite rapidly.
Because renewable depends on the weather, while nuclear doesn’t.
A mix of renewable is absolutely a good thing to do, but still, having a constant source of energy mixed with that ensure stability.
I think the issue is batteries, which are expensive and require rare earth metals which often have environmentally costly acquisition methods. Perhaps an optimal solution would be a baseline of nuclear power, and then enough renewables to meet peaks in demand. That way we have plenty of stable energy while minimizing nuclear risks.
When you get into power say a whole large city the batteries cost more then the solar panels. Especially in more polar places like Juno Alaska where you need to store a surplus of power for months. plus batteries degrade over time so they would have to be replaced. That’s part of the reason why ion flow batteries are being researched, you can just drain them and replace the fluid*.
I didn’t know about those. I’ll have to look more into it. Thanks!
last time I checked the renewables being installed didn’t even offset the new energy demands being created, let alone making a dent in starting to decarbonize existing demand.
and the main reason is, that we need to tackle climate change from as many angles as possible and not eliminate a fine energy source just because something else is cheaper.
I mean for now renewables are cheaper, do you think we have enough raw materials to cover all of earths energy needs?
what happens when the raw materials will start to run dry but we still need to cover a bunch of energy needs, is that when we dust off the good ol Nuclear plants?
not to mention Nuclear plants provide a stable base load, no need for smart electronic devices that use power when it’s most abundant etc. it’s just power, that runs, constantly.
redacted
I’m spooked by the fact that you have no idea how the US enriches uranium, or the difference between a power pressurized water reactor and a fast “breeder” reactor (if you were thinking of plutonium) or a centrifuge.
The US enriches uranium using a gas-centrifuge. The US also no longer recycles spent nuclear fuel, but France does.
redacted
Nuclear plants don’t enrich. Enrichment would happen without power plants. Bomb fuel and power fuel are not the same.
Too bad the energy companies essentially never dispose of the waste properly, because it’s too expensive if they want to give the huge bonuses to their CEOs and buyback thie stock. Even when doing it “properly” it’s basically just making it the problem of future generations once the concrete cracks.
And to reprocess the waste and make it actually safe energy would mean no profit at all plus the tech doesn’t exist yet to actually build the reactors to reprocess the waste. I mean we understand the theory, but it would take at least a decade to engineer and build a prototype.
Compare that to investing in battery tech which would have far reaching benefits. And combining that with renewables is much more profitable.
Too bad the energy companies essentially never dispose of the waste properly
To be fair, nuclear waste tends to be disposed of much more properly than coal waste.
There’s also orders of magnitudes less.
True, but still not anywhere near “clean” as it’s always marketed as.
This is a stupid take.
Coal power puts out more radioactive waste than nuclear does, and coal sends it right into the air where we can’t manage it.
Nuclear waste is kept solid, and contained. We know exactly where it goes and as long as the rules are followed it’s not at risk of polluting anything.
Sure solar and wind don’t have any by product once they are setup, but they also don’t fit the baseline power need that nuclear does.
Problem is it’s not profitable to follow the rules, and conservatives have blocked building a national “permanent” storage site for decades. The IS has no where to put it. It’s just sitting in storage facilities, above ground and in many states in places where an earthquake could cause it to leak into ground water and make the area unlivable for centuries, or cost trillions to clean up.
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/nuclear-waste-is-piling-up-does-the-u-s-have-a-plan/
Quite a large number of Republicans, including Trump himself, spend decades trying to ram Yucca mountain through. It faced heavy resistance from both the Clinton and Obama Administrations, the State of Nevada, and myriad of environmental organizations. Trying to blame it on “Conservatives” is pretty ridiculous.
https://www.ktnv.com/news/history-of-yucca-mountain-1982-2018
Yucca Mountain was killed by decades of persistent interference by opponents of nuclear power.
Yucca Mountain was a bad site. Once they started digging they found that the ground was too loose. It wouldn’t be able to support the weight without sinking. Have you ever seen the foundation of a house that sank on one side? The concrete buckles as the weight of the house slowly compacts the soil. The same thing will happen with millions of tons of waste, steel, and concrete. It’s why missile silos were built in bedrock, not loose soil. Not to mention the technology wasn’t going to allow digging deep enough to store all that much. It would mostly be used for waste from nuclear weapons, ship reactors, and other military projects. Not really that much space would have been available for commercial power generator use.
The conservatives who pushed for it did it because the contractors paid them to. It was blocked because the waste would leak not in thousands of years but in maybe decades. Not to mention the land was stolen from Native Americans and they didn’t want nuclear waste in their stollen land. Among many other issues.
Not a single power source we have is clean
How is solar, wind, or hydro not “clean”? The generating of the power, not the building of the facilities, building anything is never clean.
People count material, fuel and ecological with nuclear as well, so why not count it with hydro, wind and solar? Concrete is concrete.
Because all technology will require that. If we want energy, we have to build stuff. But there’s no fuel to buy, generally much less ecological impact due to limited waste products since no fuel is being “burned”. And the building cost is one time and generally subsidized, and maintenance is considerably lower, not to mention labor since you don’t need nuclear specialists to run the day to day.
What makes you say that. Nuclear waste has the consistency of glass or sand depending on how it’s processed. And if we reprocessed that waste like the French we could effectively remove the danger of it.
See earlier in the thread. The waste is highly radioactive, of course, and very hot for some time. First it is dumped in pools. If the pool floods or cracks, you end up with the Fukushima issue. Fortunately that went to the ocean primarily and so was diluted. But in the US, much of the country is landlocked and it would instead enter ground water.
Second, once the material is cooled enough to transport, it is supposed to be moved to a secure location, dropped deep into the ground, and encased in concrete. At this point if there are no earthquakes and water doesn’t enter and damage the concrete, this will stay put for a thousand years or so, but eventually it will get out long before it’s safe considering some of it takes around 250,000 years for it to decay enough to be safe.
As for what France does, as I mentioned, the US has not developed or built that tech because there is ultimately no profit in it and the US is unwilling to spend tax money on it. So it would fall to increased energy cost for the consumer in places where nuclear is used, and no one is going to like that. The cost of building the reprocessing facilities and doing the actual processing outweighs the value of the produced product. And building the first one is going to be the most expensive, and no modern energy company is likely to want to take the hit to short term stock prices in order to take it on. And conservatives won’t approve tax increases at all in the current political climate. And progressive places have already started moving to renewables instead since it’s cheaper.
As for what France does, as I mentioned, the US has not developed or built that tech because there is ultimately no profit in it and the US is unwilling to spend tax money on it.
First Ford, then Carter stopped commercial re-processing in the United States. Reagan brought it back. G. H. W. Bush then put the brakes on it but stopped short of an outright ban. Clinton stepped on the brakes even harder but again stopped shy of a full ban and when Bush Jr came into office he started a slow process of bringing it back. That’s as far as this CRS Report goes although there may be an updated one somewhere out there.
Still, the US has spent money on it and was doing so at least as recently as 2008. It appears the biggest worry we have is proliferation of nuclear material, not profit or cost.
The problem is that by the 80s and 90s we were trying to wind down production of nuclear weapons as the cold war was winding down. Some of these reprocessing methods, like in France, reprocess the plutonium, and modern reactors just don’t produce plutonium anymore. Also, some of the methods create uranium that is enriched to as much as 20%. With terrorism a big concern, that would be a pretty tempting target.
That being said, we are developing the tech, just very, very slowly. And now that renewables are cheap, it’s just not necessary to have so many fueled generators. So the long term profit just isn’t there for companies to want to invest. The area where I live is primarily hydro power, which is one of the more predictable renewables. But offshore wind farms give a pretty steady flow as well. And in deserts concentrated solar power can generate enough energy during the peak times when A/C is being used. And if there were better battery tech, more could be stored for use at night than currently is, and wind is still pretty reliable due to the changes in temperature from day to night.
Of course we still need fueled generators, but we shouldn’t be expanding them, we should be concentrating on using them only as a backup to renewables.
You really can’t beat clean coal
I highly, highly recommend the Oliver Stone documentary Nuclear Now from earlier this year. Completely changed my perspective. I had no idea that the oil industry was behind so much of the fear mongering around nuclear.
Whoa. Finally a state in the US that isn’t doing something completely ass backwards. We need more of this.
It’s Georgia, though. This is a positive development but it barely begins to make up for how much other ass-backwards stuff there is.
This is the state that elected Marjorie Taylor Greene, keep in mind.
A single congressional district within that state elected Marjorie Taylor Greene lol
Hopefully Georgia steps up and sticks to their guns with prosecuting people who attempt to convince election officials “to find 11,780 votes”.
This is the state that brought you Biden in 2020. And two democratic senators. Granted there’s a lot of back ass districts here, but we’re working on it I promise.
14 years and 35 billion (combined with #4 which has not been finished) and didn’t generate a single kWh in anger until now. Put the same investment into renewables and it would generate similar or greater energy and would start doing so within a year.
The argument against nuclear now is not about safety. It is about money. Nuclear simply cannot compete without massive subsidies.
Renewables and nuclear are in the same team. It’s true that nuclear requires a greater investment of money and time but the returns are greater than renewables. I recommend checking this video about the economics of nuclear energy.
That video completely ignores decommissioning costs for nuclear power plants and long-term nuclear waste storage costs in its calculation. Only in the levelized cost of electricity comparison does it show that nuclear is by far the most expensive way of generating electricity, and that it simply can’t compete with renewables on cost.
People love to look at nuclear power plants that are up and running and calculate electricity generation costs based just on operating costs - while ignoring construction costs, decommissioning costs, and waste disposal costs.
The cost of storing nuclear waste for a running plant is only a few hundred thousand a year; basically just just salary for a few people to transport it to a big hole in the ground.
Decommissioning costs a few hundred million, which sounds like a lot, but for a project that lasts for decades it’s basically nothing.
You could probably fit all of the nuclear waste America produces in few trucks. It’s not as much as people think.
Or even less if we – gasp, shock, horror! – reprocessed it.
(We don’t do that because of overblown fears about nuclear weapons proliferation.)
The Department estimates that continued operation of the current fleet of nuclear power reactors could ~70,000 metric tons of uranium * increase the total inventory of spent fuel from 70,000 metric tons of uranium to 140,000 metric tons of uranium. Nearly all of this spent fuel is being stored at the reactor sites where it was generated, either submerged in pools of water (wet storage) or in shielded casks (dry storage). The Dept of Energy
Those must be some big fucking trucks. And as far as I know, only Finland has actually developed any long-term storage which could be considered safe.
Nuclear is fine, but their takes are similar to weed fanbois, it’s not a perfect solution.
You seem to think a big number means a big pile of green goo. But actually…
All of the used fuel ever produced by the commercial nuclear industry since the late 1950s would cover a whole football field to a height of approximately 10 yards.
The question of nuclear waste, hammered home by the anti-nuclear crowd, has long since been answered. And the answer is: it’s far from being a problem.
As for the cost of storage and decommissioning, it makes no sense if we do not give a financial order of magnitude.
At French current electricity price, a 915MW reactor will produce 1.1 billion euros of electricity over one year. A 1500MW reactor will produce 1.8 billion euros of electricity over one year.
When you sell 60 billions of euros worth of electricity per year for 60 years, even if you pay 50 billions for storage and 2 billions to decommission an entire plant, it’s still quite profitable.
Estimated total cost of decommissioning in the UK is £120bn. But it’s going to take 100 years to do it… so yay lots of rotting radioactive buildings for the next century.
The nuclear waste storage facility cost 53bn to build, let alone run… so way off your ‘few hundred thousand a year’.
Does that video talk about how wind turbine blades aren’t recyclable at all so they end up in landfills? Solar panels are 75% recyclable which is excellent but that still means 25% is going into the ground. Nuclear is the only way forward.
That sound like addressable design challenges
France was able to output 2 reactors per year at 1,5 billion of euros per 1000MW for more than 2 decades during the 70’s to 90’s. The whole French nuclear industry has cost around 130-150 billions between 1960 and 2010, including researches, build and maintenance of France’s whole nuclear fleet.
A 1000MW reactor, at current French electricity price and for a 80% capacity factor, generates 1,4 billion of euros worth of electricity per year, for a minimum of 60 years.
Nuclear is not costly, and can absolutely compete by itself, if you don’t sabotage it and plan it right.
Except those reactors are off 30-50% of the time due to shoddy construction, €1.5/W in 2023 money is pure fiction, and overnight costs with free capital aren’t real costs once you adjust for inflation and stop cherry picking the first reactors before negative learning rates kicked in.
I would be very interested to know why the trend has moved away from building reactors in time and within a reasonable budget. It seems that most projects after the turn of the millennium haven’t been cost effective.
Why did we manage to build reactors well before but not now?
Every year a reactor operates is a year of experiencing new ways they suck. The fixes and added complexities are rolled into the next reactor.
Thr grifters running the show also learn new ways to grift, so the small new delays and costs are amplified.
For older reactors the costs this imposes are rolled into operational budgets (and more often than not reactors are closed as unprofitable and the public or ratepayers are left holding the bag).
Additionally regulatory agencies keep finding new instances of fraud, stopping these adds costs to the regulator and regulatee.
This has happened since well before three mile island, so all misdirections to “scare mongering about meltdowns” are lies (the rate of cost escalation actually slowed significantly after three mile island).
Base load my friend. We also need steady, reliable, clean power when it’s dark and calm. Until we can accomplish seasonal grid storage of renewables, this is the less expensive option.
There are plenty of firming options (battery, pumped hydro, flywheels etc) which deliver reliability for a fraction of the price of this boondoggle. Not to mention a diverse portfolio of renewable technologies spread over a large geographical area is actually quite stable. When the sun isn’t shining in one area, the wind may be blowing or the sun shining in another area.
Those can only hold enough power for minutes or hours.
We need to be able to store power from the summer until the winter. Months. We need to store energy from when the sun is shining in July until it’s not in December.
The only possible way to do that now is to store it as hydrogen or hydrocarbons. That infrastructure is currently very lossy, expensive, and only hypothetical.
You don’t need power storage for months, if you combine different renewable sources and have power lines connecting different areas. Wind and solar complement each other usually.
You need to be able to bridge a few weeks though, because there will be gaps, but you don’t need to store solar power for half a year to make it. It is still a big issue, but no need to exaggerate.
This idea they can only hold for minutes or hours is simply not true not to mention the entire premise is false. Only the cloudiest of days the solar panels produce 20% what they do on the sunniest days that means you only need to build out 5 times the expected output to always be able to produce what you need during sunny hourse. That means you only need to have battery backup for 16 hours. Something that’s completely feasible. The idea batteries can’t hold power for months isn’t true it’s that it’s not currently economical. How long do you think your electronics take to get from the plant to the store till you buy it and turn it on. If we’re talking about cost then let’s look at this plant. 1.1GW nuclear reactor costs 35 billion and 15 years. A solar farm built out to 5 times capacity would cost roughly 6 billion. Now triple that for battery costs if you want 24/7 electricity were on the order of 18 billion. That’s nearly half the cost and this is being very conservative assuming you want this to be a baseload supplier but will output way more most of the time. Now you will have nearly free electricity during most of the year that other industries could take advantage of like aluminum processing or something like that.
You are simply incorrect. I don’t know why you think that there are any actual technologies that can store terawatt hours of electricity for months at a time. You can’t pump storage the entirety of lake Mead. You can’t have flywheels that have such low friction at such high mass and speed. And the batteries…you can’t be serious.
You are also under the incredible misapprehension that the market is going to build excess capacity such that they will need to give away “nearly free” electricity. The need to be able to store it to sell when the price is better or be funded for some kind of (as yet hypothetical) carbon sequestration project.
Being generous with a 16h battery you already spend half overnight. What would happen in your scenario if it’s cloudy for longer than 8 hours? If it wouldn’t even last for a day it’s not a realistic plan that accounts for normal weather
- pumped hydro -> not exactly something that can be built anywhere and also not very cheap
- battery -> huge environmental impact until we can get something like sodium based batteries
- Flywheels, not exactly something that gets you through the night is it.
There’s also a reliability element too. Nuclear can reliably output a given amount of energy, at the cost of being slow to alter. Many renewable sources have sporadic amounts of power throughout each day. Either is better than fossil fuels at least.
Good point but that is not insurmountable. There are many ways to achieve predictability (batteries, hydro, tidal) that also come on stream much quicker than any nuclear plant.
Ah I’d not consider these! That gives some hope too then :) I hope we get the battery advances we need asap, the urgency from the climate crisis is strong lately.
Nuclear isn’t entirely reliable though. During the big heatwave last year at least 1 and iirc at leat a few French reactors had to be shut down because the water levels in the rivers they were on were not high enough to get sufficient water to cool them. Which is a problem that’s only going to get worse as climate change progresses.
That’s a limitation of the secondary power conversion side and is true for any power generation methodology that relies on steam generation. That said, there’s alternatives to the traditional Rankine cycle that could be deployed without modifying the nuclear side of the plant.
I don’t recall them being shut down (that would be a drastic step). They were forced to reduce output, though (making the energy more expensive).
there are a bunch of new reactor designs that don’t use water.
Renewables and nuclear play different sports.
Renewables are better for most of our needs but there is a backbone need of base power. Nuclear is an expensive but clean way to provide that.
By my very very very rough calculations, you could build a large scale solar farm with 3x power output and have enough money left over to build a 33GWh battery. That would more than cover a continuous supply of 1GW.
Absolutely, and we should. We should have both. Nuclear has a very long lifespan and very consistent power. Ideal battery setups do to buy long term lithium battery storage is less of a thing, but it’s growing. There are some other battery techs that use other chemistries which are also attractive.
Multiple eggs in multiple baskets.
Unless there are a few cloudy days in a row… My panels produce a lot less than normal during cloudy days.
Remember that blanketing the world with solar panels isn’t exactly great for the environment. Rooftops makes a lot of sense, but the cost goes way up, an maintenance becomes a nightmare. The footprint of nuclear is much smaller
The footprint of solar is significant, but still nothing compared to agriculture. E.g. The area used to grow corn to make ethanol in the US is ~ 3x what you’d need to fully power the US on solar.
~96000000 acres used for corn, ~40% of that is used for ethanol. That makes 38.3e6 acres. First estimate I found for area of solar panels to fully power the US on solar alone was 14.08e6. That makes corn for ethanol 2.7 times the area of solar panels if all that was used was solar.
What price per kw generation are you using?
The issue is that right now renewables energy don’t reduce CO2 emissions by much. (Except for hydro)
Sure if we look at the energy produced it’s very clean. The issue is intermittence. As a society we decided to continue using electrical equipment even when the sun is not shining and the wind is not blowing. So we use fossil fuel to compensate and overall the electricity production still enjoy a lot of CO2. We could use batteries, but utility scale battery are not very developed yet.
Same issue with the price. Sure solar energy is very cheap, when it’s sunny. But what if I want to turn on the light at night ? The solar panel are not producing, the wind is not blowing, price is irrelevant if I can’t get power when I need it.
Nuclear can produce a reliable amount of energy all the time.
I hope we will see the development of utility scale energy storage because this is what we really need for the development of renewable energy.
The issue is intermittence. As a society we decided to continue using electrical equipment even when the sun is not shining and the wind is not blowing.
And a lot of that can simply be solved with a larger grid.
Yes, in a small geographic area, you might run into a situation where the sun isn’t shining and the wind isn’t blowing. On the other hand, on a global scale, the sun is always shining and the wind is always blowing.
A realistic solution right now are therefore continent-wide grids that combine hydro, solar, wind and pumped hydro storage.
We don’t necessarily have to use batteries. In mountainous regions we already have stations that use surplus power to pump water up a mountain and then drop it down to generate energy when needed. Its basically a potential energy battery. But this is usually location limited and more expensive to set up.
Yes, Pump Storage Hydroelectricity is a great option for storage. It’s not the most efficient but it allows to store massive amount of energy.
I think today it’s the main utility scale storage solution in the world.
There’s also compressed air and flywheels for energy storage.
You’re describing dams, and basically all the good locations are taken already.
No, he’s describing a pumped storage facility.
Tbf that would be two dams and they did use the plural of dams, technically ‘dams’ could be a pumped storage facility.
To be even fairer, his central point that “all the good locations are taken already” only applies specifically to the regular type of dams that don’t use pumped storage. For traditional hydroelectricity you need an easily-dammed-off hilly basin containing a large/high hydraulic head river, but for pumped-storage you just need the hilly basin.
Yea you’re right.
People make stupid arguments about base load (nuclear doesn’t match supply demand so it’s meaningless argument) or renewables only being built out for maximum output = highest demand (in reality you need to build minimum output as a function of highest demand. Highest total power will far exceed highest demand and still be cheaper than fossil or nuclear. But people can’t grasp that).
Finally. Huge interconnectors like what China and Europe are doing/ done never come up.
It’s just the same old. We built 10% of renewables we need yet we are still using gas. Proof renewables don’t work!
The nuclear lobby kids never ever accept this as reality. They refused to acknowledge it in the online circles of the mid to late 90s on News Groups, early 00s on Slashdot, didn’t want to see it in the 00s on Digg, attacked any questioning nuclear the 10s and early 20s on reddit.
Every nuclear post turns into a circle jerk and a handful of people trying to ‘in before renewables’ to make sure to drown out anything that isn’t waving the nuclear flag without reservation.
We need both in some respects to maintain current electrical needs, but money and time to deploy is quantifiably much more efficient with renewables in practice vs nuclear on paper. Having a much larger renewable system spread all across the country would be of a greater short and long term benefit. Solar on every home, a small solar cell on every light pole along with low wattage monitoring systems for power distribution optimization, large desert solar installations, agrivoltaic farming (if it’s not just bullshit), wind farms in strategic areas with low impact to birds, etc.
Doing all those things would cost hundreds of times what it costs to build a reactor. There are reactors already engineered and that exist elsewhere in the world capable of powering entire cities for over a hundred years that are easily decomissionable unlike the older 1970s reactors that we have. Also renewables are unable to produce power on demand when load demands spike suddenly. U need fossil fuel for that currently. Not to mention the process of creating solar panels is one of the most environmentally damaging manufacture processes and the only country that possesses the materials to make them is China… Oil receives metric assloads of government subsidy. Why should nuclear not get the same? Nuclear power is the only thing we know of that has rhw ability to fill all of the functions that fossil fuel power plants have.Idf theres actually other options then cool but iv looked at every alternate energy source and rhw big thing that sticks out is a couple things. If the weather gets too cold, or too hot, theres a natural disaster or other condition that necessitates a very sudden and high increase in kilowatt hour demand renewable energy sources buckle. And then your left having to fire coal to meet the energy need.
Copied my comment above, sorry for the double wall of text:
Let’s play around with the thought of powering all of America with renewables. America’s coal, gas, petroleum and nuclear plants generate a combined baseload power of 405 GWavg, or “gigawatts average.” (Remember, a gigawatt is a thousand megawatts.) Let’s replace all of them with a 50 / 50 mix of onshore wind and CSP (solar), and since our energy needs are constantly growing, let’s round up the total to 500 GWs, which is likely what we’ll need by the time we finish. Some folks say that we should level off or reduce our consumption by conserving and using more efficient devices, which is true in principle. But in practice, human nature is such that whatever energy we save, we just gobble up with more gadgets. So we’d better figure on 500 GWs.
To generate this much energy with 1,000 of our 500 MW renewables farms, we’ll put 500 wind farms in the Midwest (and hope the wind patterns don’t change…) and we’ll put 500 CSP farms in the southwest deserts—all of it on free federal land and hooked into the grid. Aside from whatever branch transmission lines we’ll need (which will be chump change), here’s the lowdown:
Powering the U.S. with 500 wind and 500 CSP farms, at 500 MWavg apiece.
Steel ……………….. 503 Million tonnes (5.6 times annual U.S. production) Concrete ………….. 1.57 Billion t (3.2 times annual U.S. production) CO2 …………………. 3.3 Billion t (all U.S. passenger cars for 2.5 years) Land ………………… 91,000 km2 (302 km / side)35,135 sq. miles (169 mi / side)
(the size of Indiana)
60-year cost ……… $29.25 Trillion
That’s 29 times the 2014 discretionary federal budget.
If we can convince the wind lobby that they’re outclassed by CSP, we could do the entire project for a lot less, and put the whole enchilada in the desert:
Powering the U.S. with 1,000 CSP farms, producing 500 MWavg apiece.
Steel ………………. 787 Million t (1.6 times annual U.S. production) Concrete …………. 2.52 Billion t (5.14 times annual U.S. production) CO2 ………………… 3.02 Billion t (all U.S. passenger cars for 2.3 years) Land ……………….. 63,000 km2 (251 km / side)24,234 sq. miles (105.8 mi / side)
(the size of West Virginia)
60-year cost ……. $18.45 Trillion
#That’s to 18 times the 2014 federal budget.
Or, we could power the U.S. with 500 AP-1000 reactors.
Rated at 1,117 MWp, and with a reactor’s typical uptime of 90%, an AP-1000 will deliver 1,005 MWav. Five hundred APs will produce 502.5 GWav, replacing all existing U.S. electrical power plants, including our aging fleet of reactors.
The AP-1000 uses 5,800 tonnes of steel, 90,000 tonnes of concrete, with a combined carbon karma of 115,000 t of CO2 that can be paid down in less than 5 days. The entire plant requires 0.04km2, a patch of land just 200 meters on a side, next to an ample body of water for cooling. (Remember, it’s a Gen-3+ reactor. Most Gen-4 reactors won’t need external cooling.) Here’s the digits:
Steel ………. 2.9 Million t (0.5% of W & CSP / 0.36% of CSP) Concrete … 46.5 Million t (3.3% of W & CSP / 1.8% of CSP) CO2 ……….. 59.8 Million tonnes (2% of W & CSP / 1.5% of CSP) Land ………. 20.8 km2 (4.56 km / side) (0.028% W & CSP / 0.07% of CSP)1.95 sq. miles (1.39 miles / side)
(1.5 times the size of Central Park)
60-year cost ……… $2.94 Trillion
#That’s 2.9 times the 2014 federal budget.
Small Modular Reactors may cost a quarter or half again as much, but the buy-in is significantly less, the build-out is much faster (picture jetliners rolling off the assembly line), the resources and CO2 are just as minuscule, and they can be more widely distributed, ensuring the resiliency of the grid with multiple nodes.
And this is without even mentioning MSRs.
Was this project a complete shitshow of sheldon before seen-proportions?
Yes.
Does this mean that we should make the move towards powering the US from 100% renewables instead?
Well if you hate math and logic enough to even consider it, sure. Go ahead.
it would generate similar or greater energy and would start doing so within a year.
That’s not really accurate. There are endless lawsuits when it comes to getting windfarms going because people claim it will ruin their view or the rare redheaded blue-eyed pigeon will be hurt or some other bogus nonsense. These lawsuits can go on and on for ages.
To your point: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2022/oct/30/its-got-nasty-the-battle-to-build-the-uss-biggest-solar-power-farm https://vaenergyconsumer.com/lawsuit-aims-to-stop-massive-solar-array/ https://www.desertsun.com/story/news/environment/energy-water-summit/2017/04/21/environmentalist-just-killed-wind-farm-near-las-vegas/305796001/ https://apnews.com/article/technology-government-and-politics-environment-and-nature-las-vegas-nevada-9bf3640dfefbc6f7f45a97c6810f5ff7
Wind and Solar struggle greatly with “not in my backyard”. Of course, so too with Nuclear, and even more extreme with Nuclear, but you are correct that solar and wind have challenges with getting going.
These days EVERYTHING has like 10 lawsuits attached to it before anything can happen. Then we wonder why everything is always at a stand-still. We had a local brwery and pub in a perfect location get sued because the restuarant next door (which is kind of run down) was afraid of the competition. Now the Brewery is actually considering pulling out. Such BS especially the influx of people coming to the area would probably end up helping both businesses.
Nuclear is a waste of time and money.
Yeah, well, that’s just like, your opinion, man
Very good news. Nuclear power simply has way more benefits over fossil fuels. Not to mention it’s statistically safer, despite what decades of anti-nuclear sentiment has taught the public.
Yeah, after literally bankrupting Westinghouse and costing us Georgians billions of dollars. I’m all for more nuclear power but this project was a colossal shitshow.
Georgia also has some shiny new solar factories so I’m interested to see how deep into renewables we can get in the next decade.
The nameplate cost of this plant is $32 per watt. Even at smaller scales, utility-scale solar plants are $1 per watt. Do you know how many grid storage batteries you could buy with the extra $31 per watt? (6 hour storage is around $2.50 per watt or $.40/Wh.) You could build a solar plant 4x the nameplate capacity of the nuke (in order to match the capacity factor), and add 24 hours of storage to make it fully dispatchable, and still have enough money left over to build 2 more of the same thing. This doesn’t even include the fact the nuclear has fuel costs, waste disposal, higher continued operational costs, and unaccounted publicly involuntarily subsidized disaster insurance.
Let’s play around with the thought of powering all of America with renewables. America’s coal, gas, petroleum and nuclear plants generate a combined baseload power of 405 GWavg, or “gigawatts average.” (Remember, a gigawatt is a thousand megawatts.) Let’s replace all of them with a 50 / 50 mix of onshore wind and CSP (solar), and since our energy needs are constantly growing, let’s round up the total to 500 GWs, which is likely what we’ll need by the time we finish. Some folks say that we should level off or reduce our consumption by conserving and using more efficient devices, which is true in principle. But in practice, human nature is such that whatever energy we save, we just gobble up with more gadgets. So we’d better figure on 500 GWs.
To generate this much energy with 1,000 of our 500 MW renewables farms, we’ll put 500 wind farms in the Midwest (and hope the wind patterns don’t change…) and we’ll put 500 CSP farms in the southwest deserts—all of it on free federal land and hooked into the grid. Aside from whatever branch transmission lines we’ll need (which will be chump change), here’s the lowdown:
Powering the U.S. with 500 wind and 500 CSP farms, at 500 MWavg apiece.
Steel ……………….. 503 Million tonnes (5.6 times annual U.S. production) Concrete ………….. 1.57 Billion t (3.2 times annual U.S. production) CO2 …………………. 3.3 Billion t (all U.S. passenger cars for 2.5 years) Land ………………… 91,000 km2 (302 km / side)35,135 sq. miles (169 mi / side)
(the size of Indiana)
60-year cost ……… $29.25 Trillion
That’s 29 times the 2014 discretionary federal budget.
If we can convince the wind lobby that they’re outclassed by CSP, we could do the entire project for a lot less, and put the whole enchilada in the desert:
Powering the U.S. with 1,000 CSP farms, producing 500 MWavg apiece.
Steel ………………. 787 Million t (1.6 times annual U.S. production) Concrete …………. 2.52 Billion t (5.14 times annual U.S. production) CO2 ………………… 3.02 Billion t (all U.S. passenger cars for 2.3 years) Land ……………….. 63,000 km2 (251 km / side)24,234 sq. miles (105.8 mi / side)
(the size of West Virginia)
60-year cost ……. $18.45 Trillion
#That’s to 18 times the 2014 federal budget.
Or, we could power the U.S. with 500 AP-1000 reactors.
Rated at 1,117 MWp, and with a reactor’s typical uptime of 90%, an AP-1000 will deliver 1,005 MWav. Five hundred APs will produce 502.5 GWav, replacing all existing U.S. electrical power plants, including our aging fleet of reactors.
The AP-1000 uses 5,800 tonnes of steel, 90,000 tonnes of concrete, with a combined carbon karma of 115,000 t of CO2 that can be paid down in less than 5 days. The entire plant requires 0.04km2, a patch of land just 200 meters on a side, next to an ample body of water for cooling. (Remember, it’s a Gen-3+ reactor. Most Gen-4 reactors won’t need external cooling.) Here’s the digits:
Steel ………. 2.9 Million t (0.5% of W & CSP / 0.36% of CSP) Concrete … 46.5 Million t (3.3% of W & CSP / 1.8% of CSP) CO2 ……….. 59.8 Million tonnes (2% of W & CSP / 1.5% of CSP) Land ………. 20.8 km2 (4.56 km / side) (0.028% W & CSP / 0.07% of CSP)1.95 sq. miles (1.39 miles / side)
(1.5 times the size of Central Park)
60-year cost ……… $2.94 Trillion
#That’s 2.9 times the 2014 federal budget.
Small Modular Reactors may cost a quarter or half again as much, but the buy-in is significantly less, the build-out is much faster (picture jetliners rolling off the assembly line), the resources and CO2 are just as minuscule, and they can be more widely distributed, ensuring the resiliency of the grid with multiple nodes.
And this is without even mentioning MSRs.
Why are your only considerations concentrated solar farms and wind farms? What about hydro power, geothermal, and scattered solar installations?
Why do your numbers assume we would be building everything at once nationwide?
Why don’t you include the costs of building and running the equivalent coal plants?
It seems your comment boils down to “if we limit ourselves to implementing the most expensive options for renewables and do it on an accelerated timeframe, it’s going to cost more than if we didn’t do anything.” Not a very helpful analysis.
If you take a look at the comment that I was replying to, you will have your answer for the first question.
Because it was the scenario I chose. You are more than welcome to submit your own analysis with your own scenario and eventual limitations etc.
I didn’t include coal plants because we weren’t talking about coal plants. You are more than welcome to submit your own rundown including coal plants.
Solar is not one of the “most expensive” forms of renewable.
If you didn’t find the analysis helpful, you are once again, more than welcome to submit your own. The analysis is very helpful in the context of the comment I replied too.
If you take a look at the comment that I was replying to, you will have your answer for the first question
I didn’t include coal plants because we weren’t talking about coal plants.
So I should just ignore the first paragraph of your comment, where you introduce your own context for the rest of the comment and mention replacing coal, oil, and nuclear plants?
Let’s play around with the thought of powering all of America with renewables. America’s coal, gas, petroleum and nuclear plants generate a combined baseload power of 405 GWavg, or “gigawatts average.” (Remember, a gigawatt is a thousand megawatts.) Let’s replace all of them with a 50 / 50 mix of onshore wind and CSP (solar)
The person you replied to suggested a solar panel array. You stated you wanted to “play around with the thought of powering all of America with renewables” but then excluded all forms of renewables from your analysis except for two very specific options.
Solar is not one of the “most expensive” forms of renewable.
Who said it was? I said you chose the most expensive way of implementing it with concentrated solar power, a giant array of mirrors that focus light into a central tower. What about regular solar panel installations that don’t require a gigantic central facility hundreds of miles from population centers?
Your analysis reads like pure misinformation intent on leading people to believe our only two choices are to stick with coal, oil, and nuclear or pay multiples of our nation’s GDP and use several years worth of resources like steel in order to go the “renewable” route.
It’d be like me “playing around with the thought of powering all of America with renewables” and suggesting our only course of action with renewables is putting a giant dome over Hawaii to harness geothermal power from the active volcanoes and then running 10ft thick cables 9,000 miles across the Pacific in order to feed the mainland at a cost of 200 trillion dollars and a 100 year supply of copper. It’s an absurd and misleading proposal.
Now I am actually honestly not sure if you are actually being serious or if you are trying to troll.
“It’d be like me “playing around with the thought of powering all of America with renewables” and suggesting our only course of action with renewables is putting a giant dome over Hawaii to harness geothermal power from the active volcanoes and then running multiple 10ft thick cables 2,500 miles across the Pacific in order to feed the mainland at a cost of 200 trillion dollars and a 100 year supply of copper. It’s an absurd and misleading proposal.”
Have you been smoking crack perhaps?
Yes I could have clarified that I was discussing solar but I thought the context of the conversation was enough. But sure, “renewables” was bad formulation on my part.
The fact that you are even considering CSP shows you know nothing about the current state of renewables. What’s more likely is you’re parroting or copy-pasting some bullshit talking points from a right wing think tank. Nukes have ALWAYS gotten more expensive. I’m waiting for any production plant SMR, MSR whatever to buck this trend but it hasn’t happened.
Based and clean energy pilled.
Uh.
The nuke plant is expensive. Renewables aren’t. And your argument ist essentially “but based on made up numbers that illustrate how inexpensive nuke plants could be, nuke plants could be much less expensive! Duh!”
Yeah, no. Build renewables.
I’m not quite why the argument is “nuclear or renewables.” It should be nuclear AND renewables.
Renewable energy generators have improved significantly in the last two decades. I’m sure they will continue to improve.
Nuclear power is a hell of a lot cleaner than coal. And it seems nuclear power plants have improved tremendously. We should use them.
This right here, we could more easily transition to nuclear from coal/oil while building up the infrastructure and scale needed for renewables. In time we can phase out nuclear but at least we could have a stop gap fix in the meantime.
I take it you didn’t even bother to read my comment. So why answer it?
Solar doesn’t perform at its nameplate capacity, so you have to overbuild the capacity by about 200% in order to achieve the same baseload as a constant output thermal plant.
And that doesn’t even touch on the fact that solar doesn’t work at night, and the capacity is much lower during the different seasons in Northern latitudes.
So you either build a shitton of batteries, provide backup power sources, or tell people not to use energy during the winter. According to Tesla, they sell their Megapack batteries for around $1/watt-hour of storage. Still, lets figure a 1 Ghwr battery for every 1 GW of installed capacity of solar. That should give the system a few hours of runtime after it gets dark.
So instead of your 500 GW solar capacity, we need 1,000 GW. And 1,000 Gwhr of batteries. $68.50 Trillion worth of solar + $1 Trillion for batteries.
However, I’m a little skeptical on your solar costs. Utility scale solar is typically cited as between $1-$2/watt installed. So for 1,000 GW that gives you $1 Trillion installed. Which is a lot of money, but less than Biden’s student load forgiveness plan.
I personally believe, after spending 3 years listening to the Energy Gang podcast, that decarbonizing the energy system is an ‘all-hands on deck’ emergency that will require every trick in the book to tackle. We will likely max out every type of cheap and readily financeable energy system on this road.
Even at smaller scales, utility-scale solar plants are $1 per watt.
Solar is being built at 100% speed. We’re utilizing all the solar panel manufacturing capacity in the world building and deploying solar right now. There’s simply not enough rare earth metals to increase production more. Wind, Hydro, Nuclear and Geothermal are all needed of we want to replace coal and LNG power plants.
Thanks I posted something similar and now I can’t find the post idk if it’s the app or what but this crowd has a hard on for wasting money and taking forever to do it.
I assume the economics were quite different when they signed the contracts.
Where are you getting this “$32 per watt” number from?From googling I cannot find anything even close to that ballpark
Utility scale PV is currently around $1 to $2 a watt installed, depending on your region. Some projects have come under $1/watt.
But, you still need batteries and a solution for winter and clouds. So pumped storage, nuclear, hydrogen etc are all options.
It’s from this article: $35 billion spent / 1.1GW output = $31.8/watt
I think $31 billion would have been the more accurate number to use. There wouldn’t the same contractor buyout thing for every reactor.
It was actually $27.3 billion because the journalist was an idiot and couldn’t do math.
Wait, what? The hivemind here isn’t staunchly pro nucular?
Color me surprised.
Yay! Nuclear is the best!
Outstanding!
I’m just stoked that lemmy as a whole and I agree on. Go team.
Just in time for openheimer in IMAX!